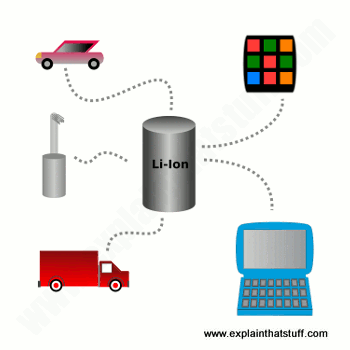
Lithium-ion batteries or li-ion cells are considered the popular choice for consumer electronics. They are testaments to how much the battery industry has continuously grown towards improvement. Though the technology behind li-ion cells has long been studied since the 1900s, it has been modified and improved drastically to maximize its performance in different industries.
Li-ion cells are typically rechargeable and are composed of cells that move electrolytes from negative to positive electrodes. Their brilliant design, low cost, and chemistry are only a few reasons why they are so popular in different industries. If you were to dissect the anatomy of a li-ion cell, you would find different kinds of elements that work together to efficiently supply the necessary power depending on the application.
The materials and elements can change the overall structure and function of a li-ion battery. Factors like energy density, longevity, and voltage all depend on the integrity of the components within each li-ion cell. This is why battery manufacturers are continuously seeking ways to improve their products by researching the best elements and materials.
History of Li-Ion Batteries
One of the most important prototypes that built the foundation for li-ion cells today is Akira Yoshino’s version back in 1985. Though this version was still further developed, it was the pioneer in lithium-ion battery technology that propelled the electric innovation we have today.
In 1991, Sony released the first commercially available lithium-ion battery and this began a whole new wave of portable gadgets that changed the way people enjoyed technology. The concept of having a type of battery that can be recharged was something that solved many problems in different industries.
Nowadays, electrification can be applied in different industries and is especially useful in the automotive sector. Li-ion cells today come in many shapes and sizes and can be made for not just cars but also boats and planes. We also use rechargeable li-ion cells for our phones and computers which is why constant innovation must be done in order to keep up with advances in modern technology.
3 Common Applications
1. Energy Storage Systems
These technologies are used to store energy when necessary. They often utilize renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. Li-ion cells are often used for these technologies since they are considered to be the most efficient and reliable in terms of application.
2. Electric Mobility
Electric mobility refers to the use of motors to enable transportation. They come in different varieties whether it’s for short or long distances. They can also be used to carry light or heavy loads depending on the li-ion cells installed within the vehicles. This includes smaller vehicles like scooters to normal, everyday cars that people use to go around to run errands.
3. Uninterruptible Power Supplies
These technologies can provide power in situations where electricity drops at an alarming rate. UPS systems are vital for places where it’s critical to keep a certain level of electrical supply such as hospitals or remote missions. Li-ion cells or batteries are often the best types of systems that can provide adequate power in these particular conditions.